How Long Does It Take To Repair A Small Epigastric Hernia In A Two Year Old
| Hernia | |
|---|---|
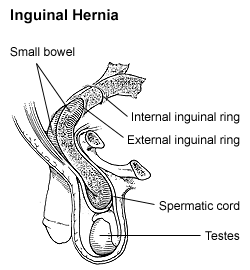 | |
| Diagram of an indirect inguinal hernia (view from the side) | |
| Specialty | General surgery |
| Symptoms | Pain especially with coughing, jutting area[1] |
| Complications | Bowel strangulation[1] |
| Usual onset | < ane year and > 50 years old (groin hernias)[two] |
| Take chances factors | Smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular illness, connective tissue disease[1] [2] [3] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, medical imaging[1] |
| Treatment | Observation, surgery[1] |
| Frequency | 18.5 million (2015)[four] |
| Deaths | 59,800 (2015)[v] |
A hernia is the aberrant exit of tissue or an organ, such equally the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which information technology normally resides.[1] Various types of hernias can occur,[half dozen] most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin.[vi] Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal type but may likewise be femoral.[1] Other types of hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias.[6] Symptoms are nowadays in well-nigh 66% of people with groin hernias.[1] This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating.[1] Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying downwardly.[1] A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down.[1] Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side.[one] The main business concern is bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to office of the bowel is blocked.[i] This usually produces severe pain and tenderness in the area.[one] Hiatus, or hiatal hernias frequently upshot in heartburn but may too cause breast pain or pain while eating.[3]
Risk factors for the development of a hernia include smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obesity, pregnancy, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease and previous open appendectomy, amid others.[1] [2] [three] Predisposition to hernias is genetic[7] and occur more ofttimes in certain families.[8] [9] [x] [1] Deleterious mutations causing predisposition to hernias seem to have ascendant inheritance (especially for men). It is unclear if groin hernias are associated with heavy lifting.[one] Hernias tin oftentimes be diagnosed based on signs and symptoms.[1] Occasionally, medical imaging is used to ostend the diagnosis or dominion out other possible causes.[1] The diagnosis of hiatus hernias is often by endoscopy.[3]
Groin hernias that do not cause symptoms in males do not need to be repaired.[ane] Repair, however, is more often than not recommended in women due to the higher rate of femoral hernias, which accept more complications.[one] If strangulation occurs, immediate surgery is required.[1] Repair may be done by open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.[one] Open surgery has the benefit of maybe beingness done nether local anesthesia rather than general anesthesia.[1] Laparoscopic surgery generally has less hurting post-obit the procedure.[ane] A hiatus hernia may be treated with lifestyle changes such as raising the head of the bed, weight loss and adjusting eating habits.[3] The medications H2 blockers or proton pump inhibitors may assist.[iii] If the symptoms practise non improve with medications, a surgery known every bit laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication may be an option.[3]
About 27% of males and iii% of females develop a groin hernia at some signal in their lives.[1] Inguinal, femoral and intestinal hernias were present in 18.v one thousand thousand people and resulted in 59,800 deaths in 2022.[4] [5] Groin hernias occur most frequently before the age of 1 and after the age of 50.[2] It is non known how normally hiatus hernias occur, with estimates in North America varying from ten% to lxxx%.[3] The first known clarification of a hernia dates dorsum to at least 1550 BC, in the Ebers Papyrus from Arab republic of egypt.[eleven]
Signs and symptoms [edit]
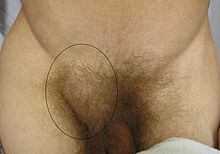
Frontal view of an inguinal hernia (right).

Incarcerated umbilical hernia with surrounding inflammation
By far the about common hernias develop in the belly when a weakness in the abdominal wall evolves into a localized hole, or "defect", through which adipose tissue, or abdominal organs covered with peritoneum, may beetle. Another mutual hernia involves the spinal discs and causes sciatica. A hiatus hernia occurs when the stomach protrudes into the mediastinum through the esophageal opening in the diaphragm.
Hernias may or may not present with either pain at the site, a visible or palpable lump, or in some cases more vague symptoms resulting from force per unit area on an organ that has go "stuck" in the hernia, sometimes leading to organ dysfunction. Fatty tissue usually enters a hernia first, but information technology may exist followed or accompanied by an organ.
Hernias are caused by a disruption or opening in the fascia, or gristly tissue, which forms the abdominal wall. It is possible for the burl associated with a hernia to come and go, but the defect in the tissue will persist.
Symptoms and signs vary depending on the type of hernia. Symptoms may or may not be present in some inguinal hernias. In the case of reducible hernias, a bulge in the groin or in some other intestinal area tin often be seen and felt. When continuing, such a burl becomes more than obvious. Besides the bulge, other symptoms include hurting in the groin that may also include a heavy or dragging sensation, and in men, there is sometimes pain and swelling in the scrotum effectually the testicular area.[12]
Irreducible abdominal hernias or incarcerated hernias may be painful, but their most relevant symptom is that they cannot return to the abdominal cavity when pushed in. They may be chronic, although painless, and tin can lead to strangulation (loss of blood supply), obstruction (kinking of intestine), or both. Strangulated hernias are always painful and pain is followed by tenderness. Nausea, vomiting, or fever may occur in these cases due to bowel obstruction. Too, the hernia bulge, in this case, may plow red, majestic or dark and pinkish.
In the diagnosis of intestinal hernias, imaging is the principal means of detecting internal diaphragmatic and other nonpalpable or unsuspected hernias. Multidetector CT (MDCT) can show with precision the anatomic site of the hernia sac, the contents of the sac, and any complications. MDCT also offers clear detail of the abdominal wall allowing wall hernias to be identified accurately.[13]
Complications [edit]
Complications may arise mail-operation, including rejection of the mesh that is used to repair the hernia. In the result of a mesh rejection, the mesh volition very likely need to exist removed. Mesh rejection can exist detected by obvious, sometimes localized swelling and pain around the mesh area. Continuous discharge from the scar is likely for a while afterwards the mesh has been removed.
A surgically treated hernia tin can lead to complications such as inguinodynia, while an untreated hernia may be complicated by:
- Inflammation
- Obstruction of any lumen, such equally bowel obstruction in intestinal hernias
- Strangulation
- Hydrocele of the hernial sac
- Hemorrhage
- Autoimmune problems
- Irreducibility or Incarceration, in which it cannot exist reduced, or pushed back into place,[14] at least non without very much external endeavour.[15] In intestinal hernias, this also substantially increases the risk of bowel obstruction and strangulation.
Causes [edit]
Causes of hiatus hernia vary depending on each individual. Among the multiple causes, however, are the mechanical causes which include: improper heavy weight lifting, difficult coughing bouts, precipitous blows to the belly, and incorrect posture.[16]
Furthermore, conditions that increase the pressure of the abdominal crenel may also cause hernias or worsen the existing ones. Some examples would exist: obesity, straining during a bowel motion or urination (constipation, enlarged prostate), chronic lung affliction, and also, fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).[17]
Also, if muscles are weakened due to poor nutrition, smoking, and overexertion, hernias are more probable to occur.
The physiological school of thought contends that in the case of inguinal hernia, the above-mentioned are just an anatomical symptom of the underlying physiological cause. They fence that the take chances of hernia is due to a physiological divergence betwixt patients who suffer hernia and those who exercise not, namely the presence of aponeurotic extensions from the transversus abdominis aponeurotic arch.[eighteen]
Abdominal wall hernia may occur due to trauma. If this type of hernia is due to edgeless trauma information technology is an emergency condition and could be associated with various solid organs and hollow viscus injuries.
Diagnosis [edit]
Inguinal [edit]
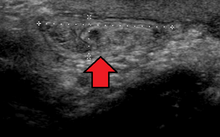
Ultrasound showing an inguinal hernia

An incarcerated inguinal hernia as seen on CT

Ten-ray of colonic herniation
By far the most common hernias (up to 75% of all intestinal hernias) are inguinal hernias, which are further divided into the more common indirect inguinal hernia (ii/3, depicted here), in which the inguinal canal is entered via a built weakness at its entrance (the internal inguinal ring), and the straight inguinal hernia type (one/3), where the hernia contents button through a weak spot in the dorsum wall of the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias are the most common blazon of hernia in both men and women. In some selected cases, they may require surgery.
There are special cases where a straight and indirect hernia appear together. A pantaloon hernia (or saddlebag hernia) is a combined direct and indirect hernia when the hernial sac protrudes on either side of the inferior epigastric vessels.
Additionally, though very rare, two or more than indirect hernias may appear together such every bit in a double indirect hernia.[xix]
Femoral [edit]
Femoral hernias occur merely below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass into the weak area at the posterior wall of the femoral canal. They can be hard to distinguish from the inguinal type (peculiarly when ascending cephalad)[ clarification needed ]: however, they generally appear more than rounded, and, in dissimilarity to inguinal hernias, at that place is a strong female person preponderance in femoral hernias. The incidence of strangulation in femoral hernias is loftier. Repair techniques are similar for femoral and inguinal hernia.
A Cooper's hernia is a femoral hernia with two sacs, the first existence in the femoral culvert, and the second passing through a defect in the superficial fascia and appearing almost immediately beneath the skin.
Umbilical [edit]
They involve protrusion of intra-abdominal contents through a weakness at the site of passage of the umbilical cord through the intestinal wall. Umbilical hernias in adults are largely caused, and are more frequent in obese or pregnant women. Abnormal decussation of fibers at the linea alba may be a contributing factor.
Incisional [edit]
An incisional hernia occurs when the defect is the result of an incompletely healed surgical wound. When these occur in median laparotomy incisions in the linea alba, they are termed ventral hernias. These tin exist the nearly frustrating and difficult to treat, equally the repair utilizes already attenuated tissue. These occur in about thirteen% of people at 2 years post-obit surgery.[20]
Diaphragmatic [edit]
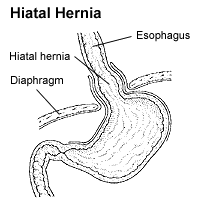
Higher in the abdomen, an (internal) "diaphragmatic hernia" results when function of the stomach or intestine protrudes into the breast crenel through a defect in the diaphragm.
A hiatus hernia is a particular variant of this type, in which the normal passageway through which the esophagus meets the stomach (esophageal hiatus) serves every bit a functional "defect", allowing part of the breadbasket to (periodically) "herniate" into the chest. Hiatus hernias may exist either "sliding", in which the gastroesophageal junction itself slides through the defect into the chest, or non-sliding (also known as para-esophageal), in which case the junction remains stock-still while some other portion of the stomach moves upwardly through the defect. Non-sliding or para-esophageal hernias can be dangerous as they may allow the tum to rotate and obstruct. Repair is usually advised.
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a distinct problem, occurring in upwards to 1 in 2000 births, and requiring pediatric surgery. Intestinal organs may herniate through several parts of the diaphragm, posterolateral (in Bochdalek's triangle (lumbocostal triangle), resulting in a Bochdalek hernia), or anteromedial-retrosternal (in the scissure of foramina of Morgagni (sternocostal triangle), resulting in a Morgagni's hernia).[21]
Other hernias [edit]
Since many organs or parts of organs can herniate through many orifices, it is very hard to give an exhaustive list of hernias, with all synonyms and eponyms. The above article deals mostly with "visceral hernias", where the herniating tissue arises within the abdominal cavity. Other hernia types and unusual types of visceral hernias are listed beneath, in alphabetical order:
- Abdominal wall hernias:
- Umbilical hernia
- Epigastric hernia: a hernia through the linea alba higher up the umbilicus.
- Spigelian hernia, besides known every bit spontaneous lateral ventral hernia
- Amyand's hernia: containing the appendix vermiformis within the hernia sac
- Brain herniation, sometimes referred to equally brain hernia, is a potentially deadly side effect of very high intracranial pressure level that occurs when a function of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull.
- Wide ligament hernia, of the uterus.[22] [23]
- Double indirect hernia: an indirect inguinal hernia with 2 hernia sacs, without a concomitant direct hernia component (as seen in a pantaloon hernia).[19]
- Hiatus hernia: a hernia due to "short oesophagus" — insufficient elongation — stomach is displaced into the thorax
- Littre's hernia: a hernia involving a Meckel'south diverticulum. It is named subsequently the French anatomist Alexis Littré (1658–1726).
- Lumbar hernia: a hernia in the lumbar region (non to be dislocated with a lumbar disc hernia), contains the post-obit entities:
- Petit's hernia: a hernia through Petit's triangle (inferior lumbar triangle). It is named subsequently French surgeon Jean Louis Petit (1674–1750).
- Grynfeltt's hernia: a hernia through Grynfeltt-Lesshaft triangle (superior lumbar triangle). Information technology is named after doctor Joseph Grynfeltt (1840–1913).
- Maydl's hernia: ii next loops of pocket-sized intestine are within a hernial sac with a tight neck. The intervening portion of bowel within the abdomen is deprived of its blood supply and eventually becomes necrotic.
- Obturator hernia: hernia through obturator canal
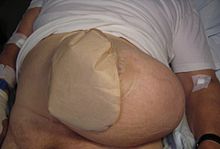
Patient with a colostomy complicated by a big parastomal hernia.
- Parastomal hernias, which is when tissue protrudes adjacent to a stoma tract.
- Paraumbilical hernia: a type of umbilical hernia occurring in adults
- Perineal hernia: a perineal hernia protrudes through the muscles and fascia of the perineal floor. It may be primary merely commonly is acquired following perineal prostatectomy, abdominoperineal resection of the rectum, or pelvic exenteration.
- Properitoneal hernia: rare hernia located directly above the peritoneum, for example, when part of inguinal hernia projects from the deep inguinal ring to the preperitoneal space.
- Richter's hernia: a hernia involving only one sidewall of the bowel, which tin effect in bowel strangulation leading to perforation through ischaemia without causing bowel obstacle or whatsoever of its warning signs. It is named afterwards German surgeon Baronial Gottlieb Richter (1742–1812).
- Sliding hernia: occurs when an organ drags along part of the peritoneum, or, in other words, the organ is role of the hernia sac. The colon and the urinary bladder are often involved. The term also ofttimes refers to sliding hernias of the stomach.
- Sciatic hernia: this hernia in the greater sciatic foramen well-nigh commonly presents equally an uncomfortable mass in the gluteal surface area. Bowel obstruction may likewise occur. This type of hernia is only a rare cause of sciatic neuralgia.
- Sports hernia: a hernia characterized by chronic groin pain in athletes and a dilated superficial inguinal ring.
- Tibialis inductive hernia: tin nowadays as a bulge in the shins. Pain on residual, walking, or during exercise may occur. The burl can typically not exist nowadays unless force per unit area or flexing of the leg occurs.[24] [25] [26]
- Velpeau hernia: a hernia in the groin in front of the femoral blood vessels
Treatment [edit]

Truss [edit]
The benefits of the apply of an external device to maintain reduction of the hernia without repairing the underlying defect (such as hernia trusses, trunks, belts, etc.) are unclear.[one]
Surgery [edit]
Surgery is recommended for some types of hernias to prevent complications such every bit obstruction of the bowel or strangulation of the tissue, although umbilical hernias and hiatus hernias may be watched, or are treated with medication.[27] Most abdominal hernias can be surgically repaired, just surgery has complications. Time needed for recovery after treatment is reduced if hernias are operated on laparoscopically. However, open surgery tin be done sometimes without general anesthesia. Robot-assisted hernia surgery has also recently gained popularity as safe alternatives to open surgery.
Uncomplicated hernias are principally repaired past pushing back, or "reducing", the herniated tissue, and so mending the weakness in muscle tissue (an operation called herniorrhaphy). If complications have occurred, the surgeon volition check the viability of the herniated organ and remove part of it if necessary.
Musculus reinforcement techniques frequently involve synthetic materials (a mesh prosthesis).[28] The mesh is placed either over the defect (anterior repair) or nether the defect (posterior repair). At times staples are used to keep the mesh in place. These mesh repair methods are often chosen "tension free" repairs considering, unlike some suture methods (e.g., Shouldice), muscle is not pulled together under tension. However, this widely used terminology is misleading, as at that place are many tension-free suture methods that do not use mesh (e.m., Desarda, Guarnieri, Lipton-Estrin, etc.).
Bear witness suggests that tension-free methods (with or without mesh) often have lower percent of recurrences and the fastest recovery menstruation compared to tension suture methods. Even so, among other possible complications, prosthetic mesh usage seems to accept a college incidence of chronic pain and tin can besides cause infections.[29]
The frequency of surgical correction ranges from 10 per 100,000 (U.1000.) to 28 per 100,000 (U.S.).[1]
Recovery [edit]
Many patients are managed through day surgery centers and are able to render to work within a week or two, though intense activities are prohibited for a longer flow. People who have their hernias repaired with mesh often recover within a calendar month, simply pain can last longer. Surgical complications may include pain that lasts more than 3 months, surgical site infections, nerve and claret vessel injuries, injury to nearby organs, and hernia recurrence. Pain that lasts more than 3 months occurs in about 10% of people post-obit hernia repair.[1]
Epidemiology [edit]
Nigh 27% of males and 3% of females develop a groin hernia at some time in their lives.[1] In 2022 about 25 million people had a hernia.[thirty] Inguinal, femoral and abdominal hernias resulted in 32,500 deaths globally in 2022 and 50,500 in 1990.[31]
References [edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m due north o p q r s t u v w ten y z aa ab ac ad Fitzgibbons RJ, Forse RA (February 2022). "Clinical practice. Groin hernias in adults". The New England Journal of Medicine. 372 (eight): 756–63. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1404068. PMID 25693015.
- ^ a b c d Domino FJ (2014). The five-infinitesimal clinical consult 2022 (22nd ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 562. ISBN9781451188509. Archived from the original on 2022-08-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Roman Due south, Kahrilas PJ (October 2022). "The diagnosis and management of hiatus hernia". BMJ. 349: g6154. doi:10.1136/bmj.g6154. PMID 25341679. S2CID 7141090.
- ^ a b Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (GBD 2022 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (October 2022). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Illness Study 2022". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:x.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-vi. PMC5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ a b Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al. (GBD 2022 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (October 2022). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and crusade-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2022". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(sixteen)31012-1. PMC5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ a b c "Hernia". MedlinePlus. U.Southward. National Library of Medicine. 9 August 2022. Archived from the original on sixteen March 2022. Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ Öberg Due south, Andresen K, Rosenberg J (2017). "Etiology of Inguinal Hernias: A Comprehensive Review". Frontiers in Surgery. four: 52. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2017.00052. PMC5614933. PMID 29018803.
- ^ Mihailov E, Nikopensius T, Reigo A, Nikkolo C, Kals M, Aruaas K, et al. (February 2022). "Whole-exome sequencing identifies a potential TTN mutation in a multiplex family with inguinal hernia". Hernia. 21 (1): 95–100. doi:10.1007/s10029-016-1491-9. PMC5281683. PMID 27115767.
- ^ Sezer S, Şimşek N, Celik HT, Erden Yard, Ozturk G, Düzgün AP, et al. (August 2022). "Association of collagen type I blastoff 1 gene polymorphism with inguinal hernia". Hernia. xviii (4): 507–12. doi:10.1007/s10029-013-1147-y. PMID 23925543. S2CID 22999363.
- ^ Gong Y, Shao C, Sun Q, Chen B, Jiang Y, Guo C, et al. (March 1994). "Genetic study of indirect inguinal hernia". Periodical of Medical Genetics. 31 (three): 187–92. doi:10.1136/jmg.31.three.187. PMC1049739. PMID 8014965.
- ^ Nigam VK (2009). Essentials of Abdominal Wall Hernias. I. K. International Pvt Ltd. p. 6. ISBN9788189866938. Archived from the original on 2022-09-08.
- ^ "Inguinal hernia". The Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 2022-02-13. Retrieved 2010-05-24 .
- ^ Lee HK, Park SJ, Yi BH (2010). "Multidetector CT reveals various multifariousness of intestinal hernias". Diagnostic Imaging. 32 (v): 27–31. Archived from the original on 2022-06-xviii. Retrieved 2010-06-25 .
- ^ Goers TA, Klingensmith ME, Chen LE, Glasgow SC (2008). The Washington transmission of surgery. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN978-0-7817-7447-5.
- ^ "Incarcerated". onlinedictionary.datasegment.com. Archived from the original on 2008-xi-20. Citing: Webster 1913
- ^ "Hiatal Hernia Symptoms, Causes And Relation To Acrid Reflux And Heartburn". Archived from the original on October 28, 2008. Retrieved 2010-05-24 .
- ^ Balentine JR. Stöppler MC (ed.). "Hernia Causes". eMedicineHealth.com. WebMD. Archived from the original on 2022-05-31. Retrieved 2010-05-24 .
- ^ Desarda MP (April 2003). "Surgical physiology of inguinal hernia repair--a study of 200 cases". BMC Surgery. three: ii. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-3-ii. PMC155644. PMID 12697071.
- ^ a b Jones R (2013). "An unexpected finding during an inguinal herniorrhaphy: written report of an indirect hernia with two hernia sacs". Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports. one (x): 331–332. doi:10.1016/j.epsc.2013.09.002.
- ^ Bosanquet DC, Ansell J, Abdelrahman T, Cornish J, Harries R, Stimpson A, et al. (2015). "Systematic Review and Meta-Regression of Factors Affecting Midline Incisional Hernia Rates: Analysis of xiv,618 Patients". PLOS One. 10 (9): e0138745. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1038745B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138745. PMC4577082. PMID 26389785.
- ^ Arráez-Aybar LA, González-Gómez CC, Torres-García AJ (May 2009). "Morgagni-Larrey parasternal diaphragmatic hernia in the developed". Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas /. 101 (5): 357–66. PMID 19527083.
- ^ Ozben 5, Aliyeva Z, Barbur E, Guler I, Karahasanoglu T, Baca B (September 2022). "Laparoscopic management of incarcerated broad ligament hernia in a patient with bilateral parametrium defects - a video vignette". Colorectal Illness. 22 (9): 1197–1198. doi:10.1111/codi.15039. PMID 32180330. S2CID 212739555.
- ^ Hiraiwa One thousand, Morozumi K, Miyazaki H, Sotome 1000, Furukawa A, Nakamaru Thousand (March 2006). "Strangulated hernia through a defect of the broad ligament and mobile cecum: a case study". Globe Journal of Gastroenterology. 12 (9): 1479–fourscore. doi:ten.3748/wjg.v12.i9.1479. PMC4124335. PMID 16552826.
- ^ Nguyen JT, Nguyen JL, Wheatley MJ, Nguyen TA (2013). "Muscle hernias of the leg: A case report and comprehensive review of the literature". The Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery. 21 (4): 243–vii. doi:10.1177/229255031302100408. PMC3910527. PMID 24497767.
- ^ Masoumi A, Ramogida M (April 2022). "Tibialis anterior herniation - a rare clinical entity: a case report and review of the literature". The Periodical of the Canadian Chiropractic Association. 64 (1): 88–91. PMC7250514. PMID 32476672.
- ^ Sharma N, Kumar Due north, Verma R, Jhobta A (2017-05-31). "Tibialis Inductive Muscle Hernia: A Case of Chronic, Ho-hum Hurting and Swelling in Leg Diagnosed by Dynamic Ultrasonography". Smooth Journal of Radiology. 82: 293–295. doi:10.12659/PJR.900846. PMC5462483. PMID 28638493.
- ^ "Hernia". U.One thousand. National Health Service. Archived from the original on 2022-07-fourteen. Retrieved 2017-07-23 .
- ^ Kamtoh G, Pach R, Kibil W, Matyja A, Solecki R, Banas B, Kulig J (September 2022). "Effectiveness of mesh hernioplasty in incarcerated inguinal hernias". Wideochirurgia I Inne Techniki Maloinwazyjne = Videosurgery and Other Miniinvasive Techniques. 9 (3): 415–nine. doi:10.5114/wiitm.2014.43080. PMC4198637. PMID 25337167.
- ^ Sohail MR, Smilack JD (June 2004). "Hernia repair mesh-associated Mycobacterium goodii infection". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 42 (six): 2858–60. doi:10.1128/JCM.42.6.2858-2860.2004. PMC427896. PMID 15184492.
- ^ Vos T, Hairdresser RM, Bell B, Bertozzi-Villa A, Biryukov Due south, Bolliger I, et al. (Global Burden of Disease Study 2022 Collaborators) (August 2022). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2022". Lancet. 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-iv. PMC4561509. PMID 26063472.
- ^ Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A, Liang X, Zhou K, et al. (GBD 2022 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (Jan 2022). "Global, regional, and national age-sexual practice specific all-cause and crusade-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic assay for the Global Burden of Disease Written report 2022". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:x.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-two. PMC4340604. PMID 25530442.
External links [edit]
| | Wait up hernia in Wiktionary, the costless lexicon. |
| | Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hernias. |
- Hernia at Curlie
- "hernia". MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hernia
Posted by: hebronventis.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Long Does It Take To Repair A Small Epigastric Hernia In A Two Year Old"
Post a Comment